Introduction
Parasympathetic ganglia are the cluster of neurons that receive preganglionic inputs and can exhibit reflex activity independently of the CNS. In the head and neck region, there are 4 parasympathetic ganglia present bilaterally. They are:
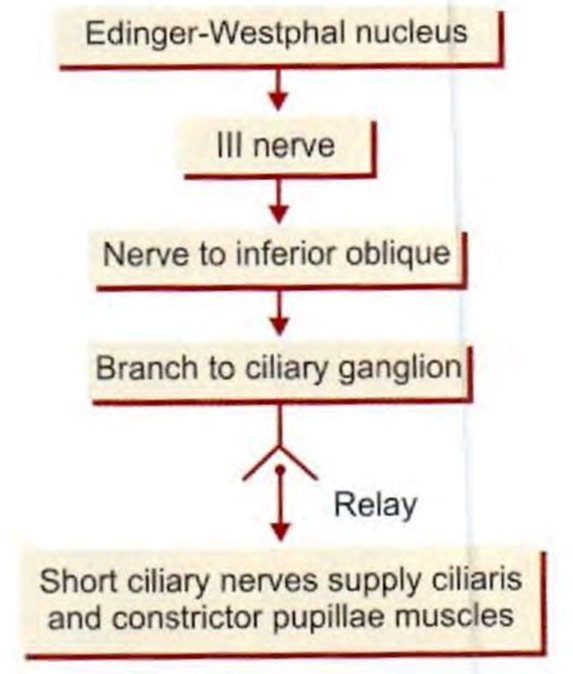
Ciliary ganglion
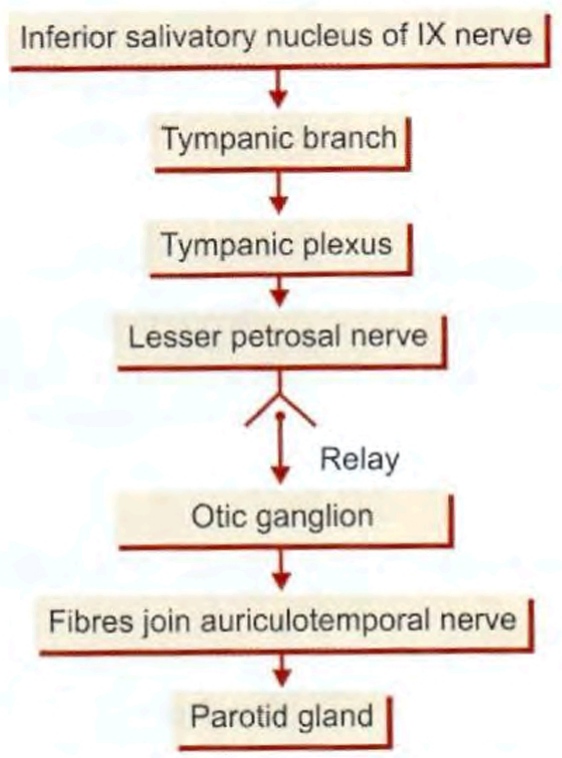
Otic ganglion
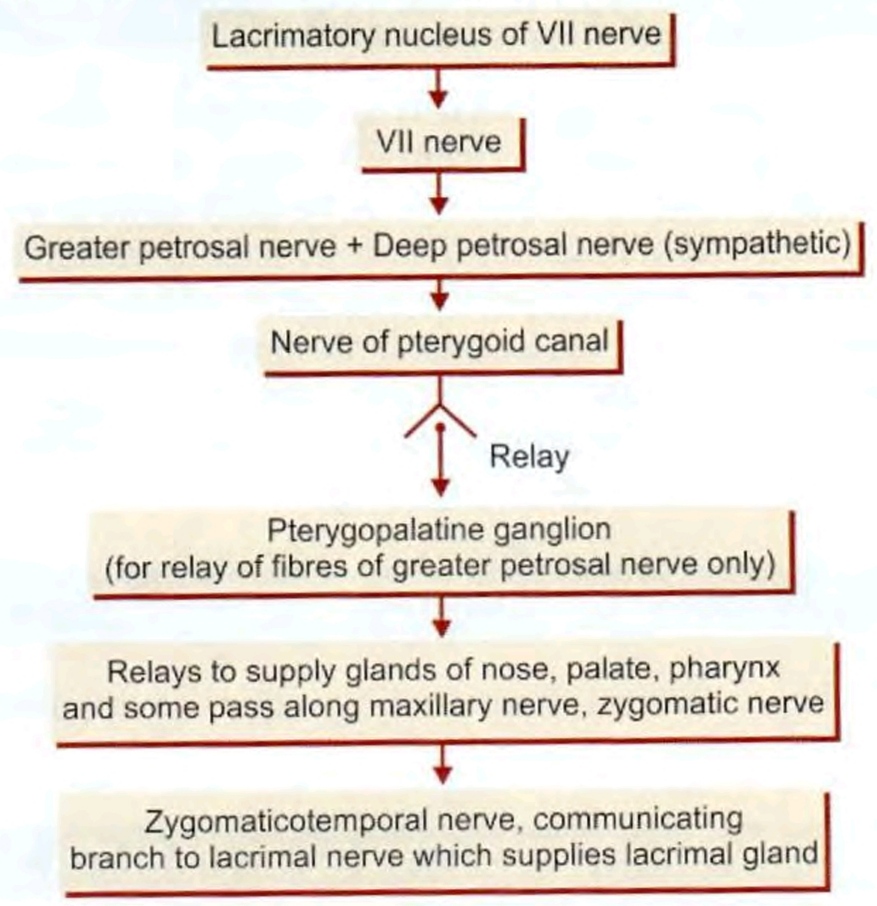
Pterygopalatine ganglion
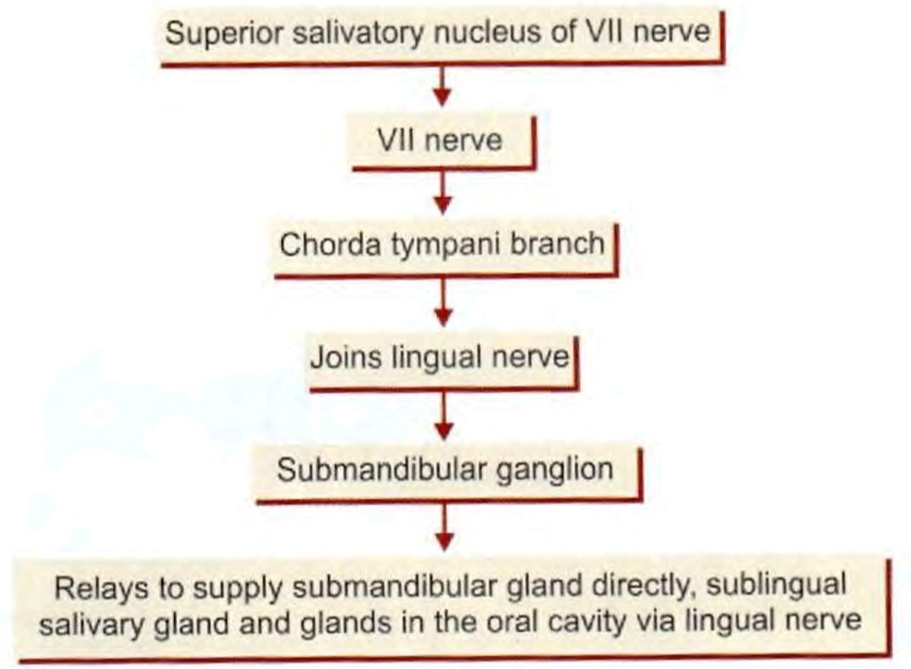
Submandibular ganglion
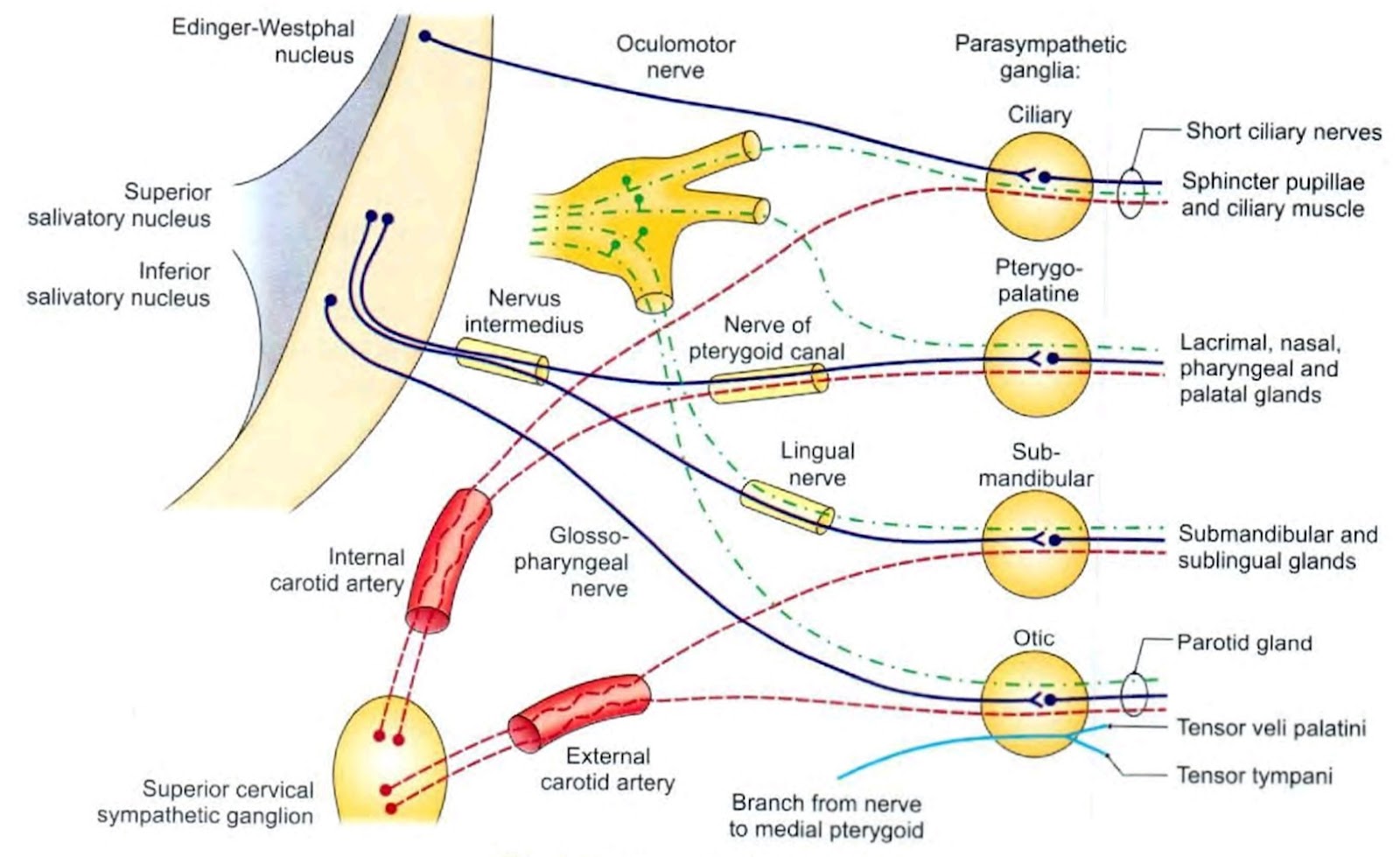
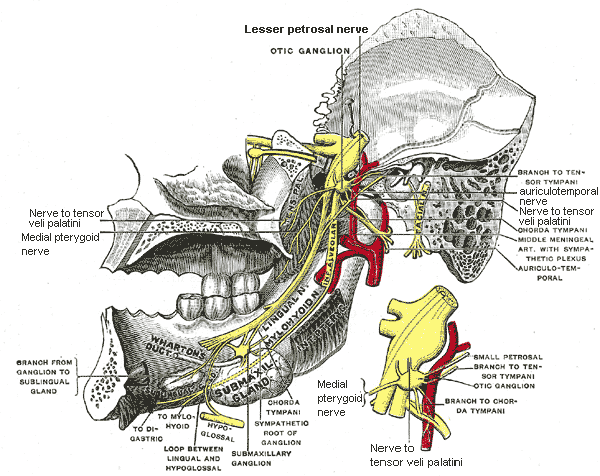
Submandibular and otic ganglion - relation
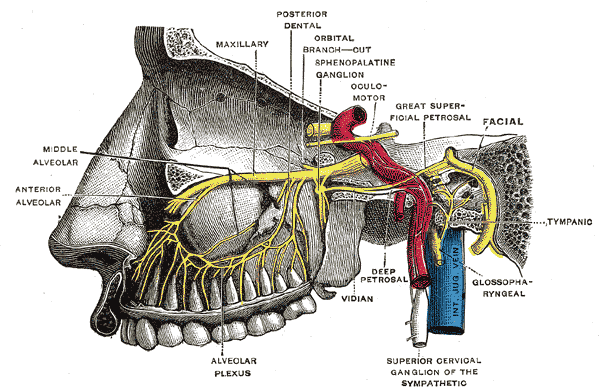
Pterygopalatine ganglion - relation
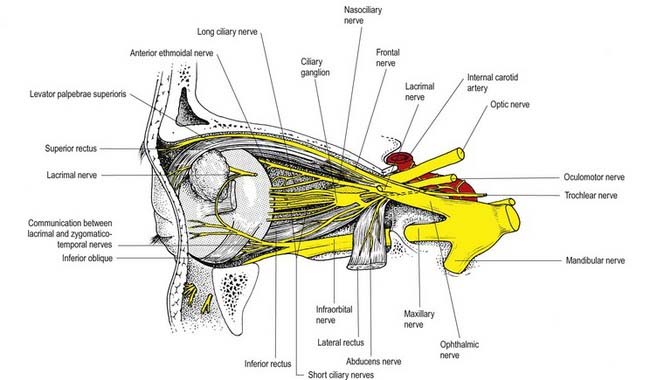 Ciliary ganglion - relation
Ciliary ganglion - relation
| Submandibular ganglion | Pterygopalatine ganglion / ganglion of Hay fever | Otic ganglion | Ciliary ganglion |
Location | Superficial to hyoglossus | In the pterygopalatine fossa | In the infratemporal fossa | Apex of orbit |
Topographic relation | Lingual nerve | Maxillary nerve | Auriculotemporal nerve | Nasociliary nerve |
Function relation | Facial nerve | Facial nerve | Glossopharyngeal nerve | Occulomotor nerve |
Sensory root | Lingual nerve | Maxillary nerve | Auriculotemporal nerve | Nasociliary nerve |
Sympathetic root | Plexus around facial artery | Plexus around internal carotid artery through deep petrosal nerve | Plexus along middle meningeal artery | Plexus around ophthalmic artery |
Distribution | Submandibular, sublingual and anterior lingual glands | Mucus glands or nose, sinuses, palate, nasopharynx; lacrimal glands | Parotid gland | Ciliary muscles and sphincter pupillae |
Parasympathetic roots
Submandibular ganglion
Pterygopalatine ganglion
Otic ganglion
Ciliary ganglion
Reference:
Textbook of Anatomy - Head and Neck by B D Chaurasia
Ciliary ganglion - relation

1 comment